|
|
|
 |
RADON |  |
|
Radon atom |
|
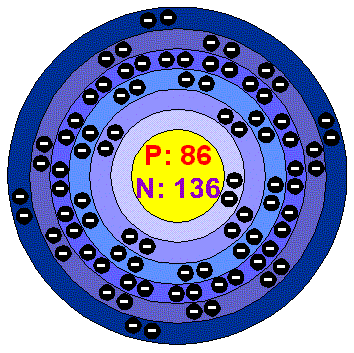 |
The Basics: Name: radon Symbol: Rn Atomic number: 86 Atomic weight: [222.02] CAS Registry ID:10043-92-2 Group number:18 Group name:Noble gas Period number: 6 Block: p-block |
| Description: At ordinary temperatures radon is a colourless gas. When cooled below the freezing point, radon exhibits a brilliant phosphorescence which becomes yellow as the temperature is lowered and orange-red at the temperature of liquid air. The main hazard is from inhalation of the element and its decay products which are collected on dust in the air. Recently, radon buildup in homes from the surrounding soil and rocks has become a safety issue and some areas around the world test homes for radon gas. It is the heaviest known gas. Radon is present in some spring waters. |
|
|
|
Isolation: Radon is present to a very small trace extent in the atmosphere and in principle could be obtained as a byproduct from the liquefaction and separation of air. However as only small quantities are ever needed in practice, and because of its short half life (the longest life isotope has a half life of less than 4 days), such quantities as are required are isolated through collection from the radioactive decay of an isotope of radium (226Ra, half life 1599 years). |
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|